4th August 2016
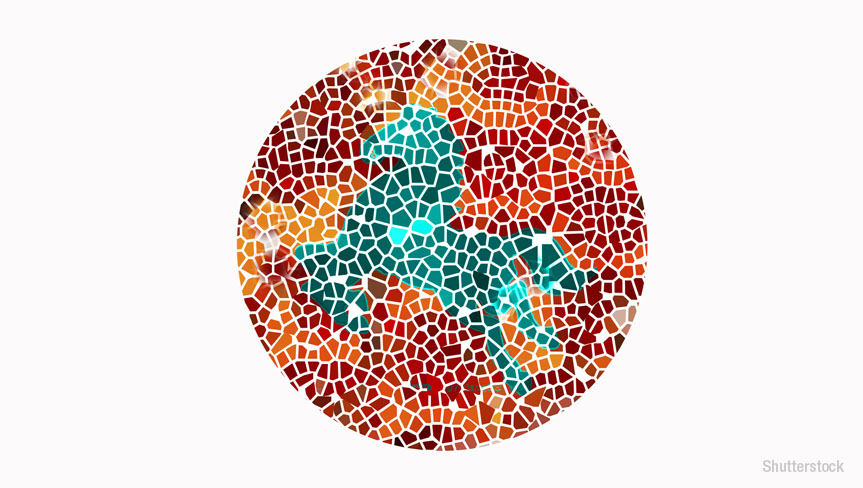
What is colour-blindness and why does it occur?
Colour-blindness, also known as colour vision deficiency, is the inability of the human eye to see or differentiate between colours. This optical condition, which is mostly genetic, occurs due to a fault in the development of cone cells present in the eye. Cone cells and rod cells, present in the retinal section, ensure colour vision and night and low-light vision respectively.
• • •