20th May 2016
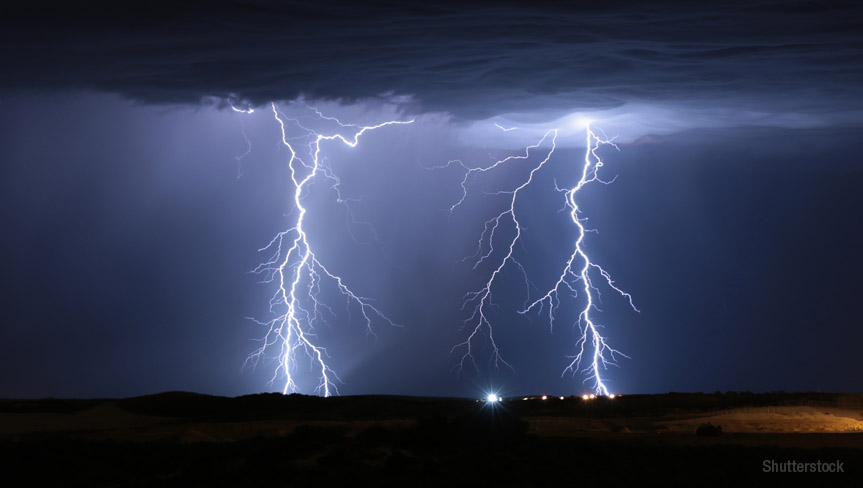
100 lightning bolts strike the earth every second
Lightning bolts are electric discharges that originate in the clouds during a storm and travel to the earth’s surface. About 100 lightning bolts strike the earth every second. One bolt can contain up to one billion volts of electricity.